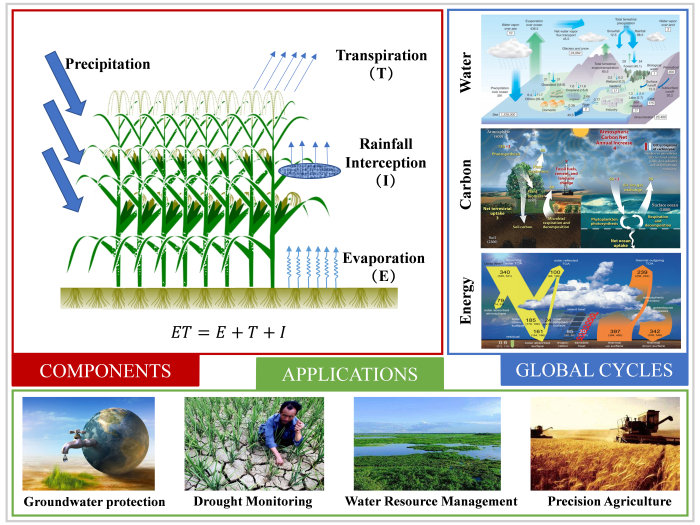
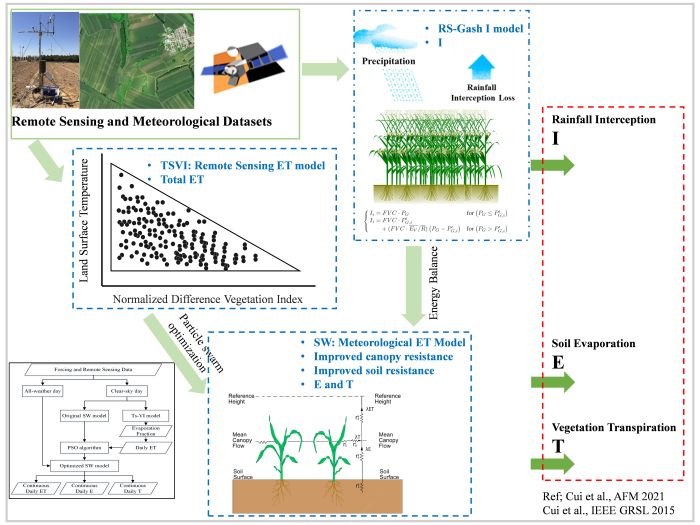
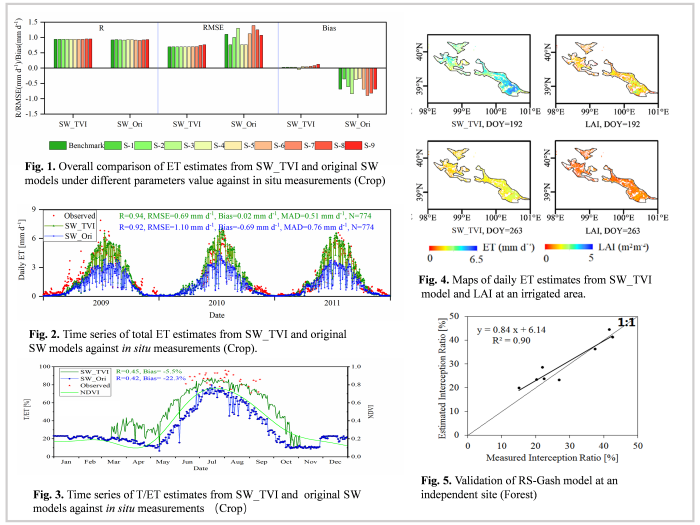
A Coupled Evapotranspiration Model by Integrating Remote Sensing- and Meteorology-Based Models
Based on the remote sensing-based vegetation rainfall interception model at regional scale (RS-Gash), an coupled evapotranspiration (ET) model was developed (named SW_TVI) using the particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm to integrate the original Shuttleworth-Wallace model (SW) and the surface temperature-vegetation index (Ts-VI) triangle model. All components of the ET can be obtained at large scale, including soil evaporation (E), vegetation transpiration (T) and rainfall interception (I). The accuracy of total ET estimates is 0.69 mm/day, bias of the T/ET ratio is -5.5%, and accuracy of I/P (Precipitation) ratio is less than 5%. This will benefit groundwater protection, drought monitoring, water resources management, and precision agriculture development.